Woody Invasive Species Resources

The Woody Invasives Working Group (WIWG) was funded in the 2023 grant cycle by the MT Noxious Weed Trust Fund to develop a statewide management plan for common buckthorn, Russian olive, and saltcedar. Projects completed during this time were educational materials that specified identification and control options through the year for all three target species and additional outreach on online and radio platforms to outdoor enthusiasts and landowners. Within the statewide management plan, goals include identifying stable funding and continued efforts toward outreach and education. As part of this, the Core Planning Group is organizing a river tour to view past projects and positive outcomes from control projects, educating on how important funding is for this type of work, and continuing with biannual partner update meetings.
Upcoming Events:
March 24, 2026 WIWG Meeting, Calvert Hotel, Lewistown
July 16, 2026 WIWG River Tour, Billings
Review the Draft Woody Invasives Statewide Management Plan.
The public comment period for this draft plan is now closed.
Help Montana by learning how to identify and report woody invasive species.

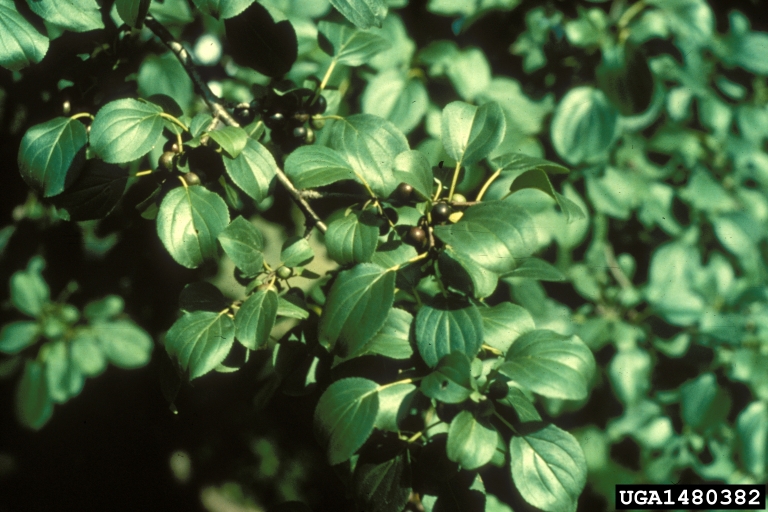
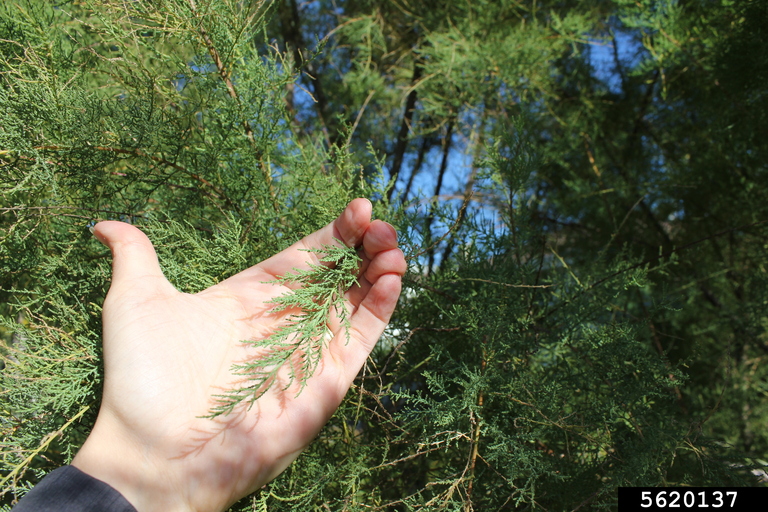
Common Buckthorn (Rhamnus cathartica)
A large shrub or small tree (6-20ft tall) that has deciduous leaves which remain green long into the fall compared to native species. It can develop into dense monocultures, reduce habitat, and outcompete native species.
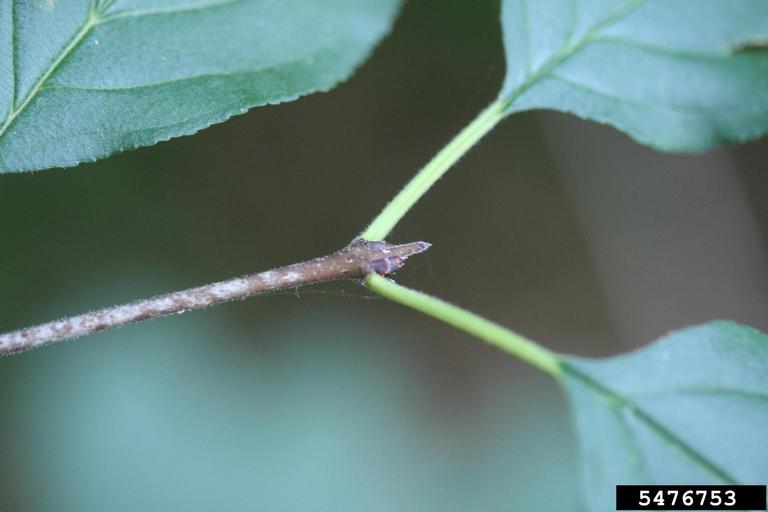


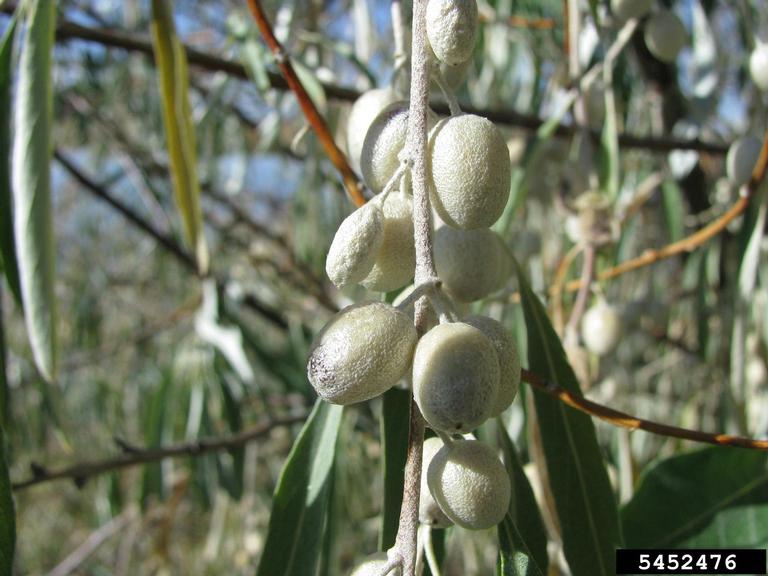
Russian Olive (Elaeagnus angustifolia)
A tall shrub or small tree (up to 26ft tall) wth branches that are orange-brown in color with white-mealy hairs. Readily invades riparian habitat, outcompeting native species and alters the ecosystem.
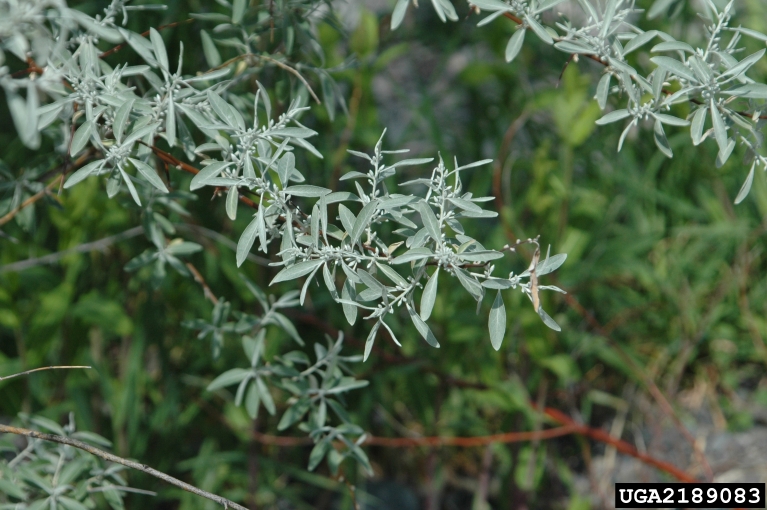


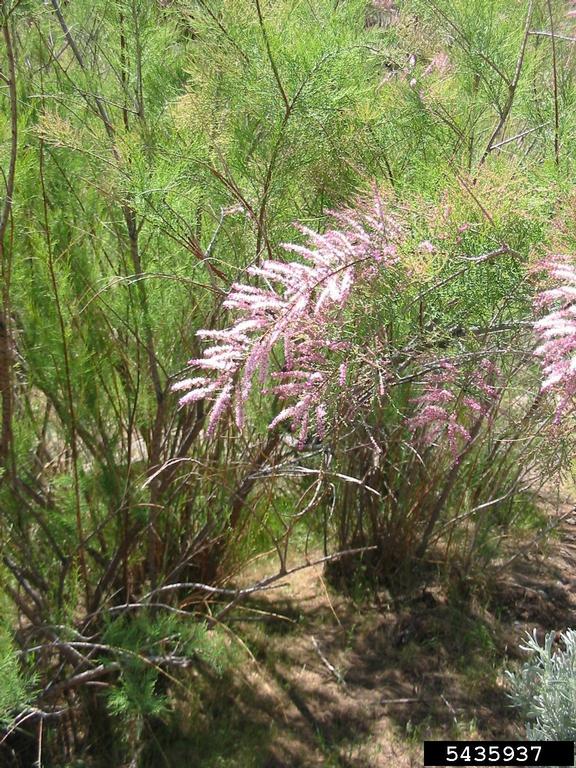
Saltcedar (Tamarix chinensis, T. ramosissima and hybrids)
Wispy shrubby growth form (3-17ft tall) that often occurs in riparian areas. Has short clusters of tiny pink flowers that cover the shrub during the growing season. Crowds out native species and chokes riparian corridors.


Reporting woody invasive species helps us prioritize management across watersheds.
Contact your local extension agent
Contact your local weed district
Reporting best practices include clear photos and detailed location information.
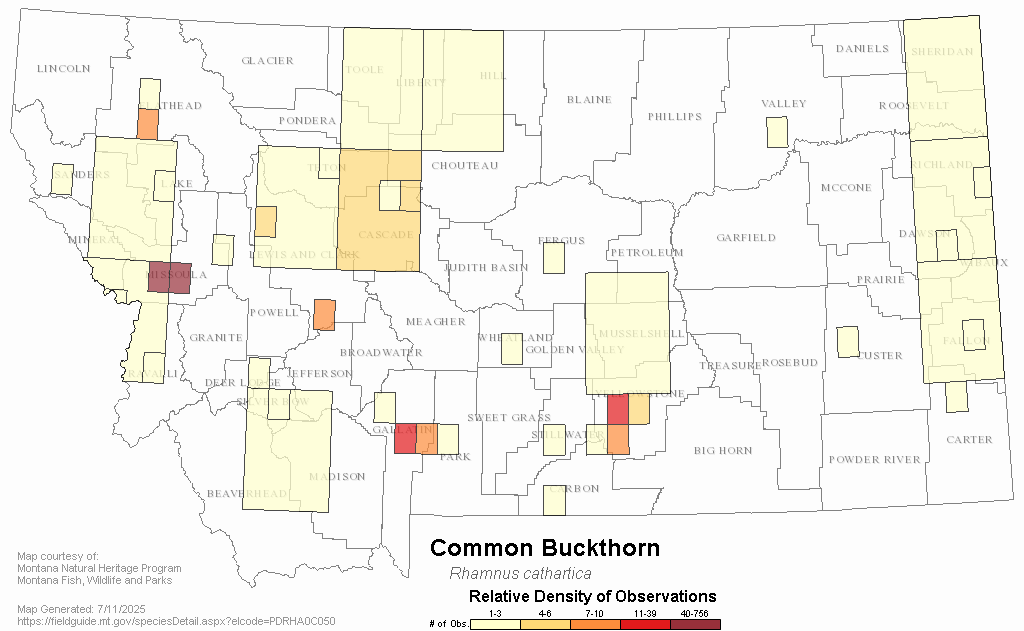
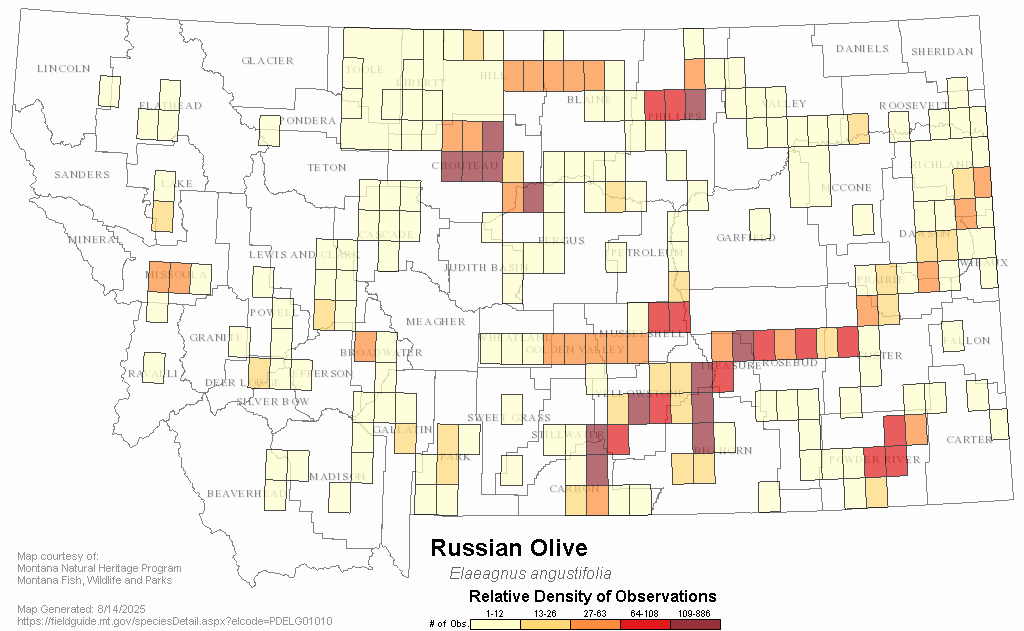
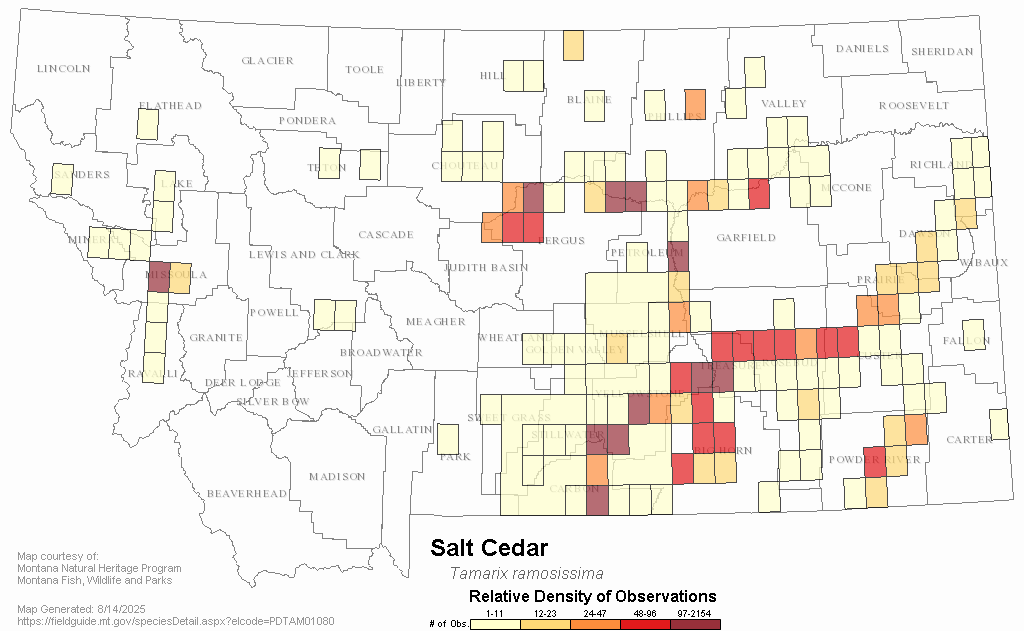
Woody invasive species have broad negative impacts to water quality, wildlife and fisheries habitat, agricultural production, recreation, and property values. Management is a shared responsibility among all land and water users.



